Annotations
- Introduction
- Struts Convention Plugin
- Struts Configuration Plugin
- Annotations
- Struts Configuration Values
- Summary
The example code for this tutorial, annotations, is available for checkout at struts-examples
Introduction
In our previous tutorials we’ve been using an XML file (struts.xml) to configure our applications. The XML file wires
up the action names (register), with ActionSupport classes (RegisterAction.java), and with the result to render back
to the browser (register.jsp). Struts provides an alternative to using XML to configure your application by using
standard naming conventions and annotations for your action names, ActionSupport classes, and results.
This tutorial assumes you understand how to apply annotations to Java classes and methods. If you’re not familiar with annotations, consult the Java online tutorial.
The Struts user mailing list is an excellent place to get help. If you are having a problem getting the tutorial example applications to work search the Struts mailing list. If you don’t find an answer to your problem, post a question on the mailing list.
Struts Convention Plugin
Struts enables the use of standard naming conventions and annotations when you include the Convention plugin in your application’s class path. If you’re using Maven you’ll need to add a dependency:
Convention Plugin Dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.struts</groupId>
<artifactId>struts2-convention-plugin</artifactId>
<version>X.X.X.X</version>
</dependency>
If you’re using Ant then copy the struts2-convention-plugin jar file from the Struts download to your WEB-INF/lib folder.
The convention plugin provide several different ways you can configure your Struts application without using XML. Consult the Convention Plugin documentation for complete details. This tutorial only examines one simple way of following the conventions provided by the Convention plugin.
When you run the example application you’ll see on the index.jsp page a link to Get your hello. This URL for the link
is hello.action. When you click on this link, the execute method of class HelloAction.java (which is a Struts ActionSupport class)
is run. The view page rendered back to the browser after the execute method returns success is hello-success.jsp.
None of the above is wired up using XML but rather happens because the application follows the standard naming conventions
expected by the Convention plugin. The first convention is that the ActionSupport class, HelloAction.java, is in package
org.apache.struts.struts2annotations.action. One of the Convention plugin’s defaults is to look for ActionSupport
classes that are in package structure that ends in action. The next convention the application follows is that HelloAction.java
extends the ActionSupport class and defines an execute method. The link is hello.action. When the Struts filter sees
a request for hello.action it will map that request to the HelloAction class’s execute method due to the Convention
plugin being used.
So a link of hello.action causes the execute method of class HelloAction to be run. That method returns success.
Because the application is using the Convention plugin, Struts will render back to the browser a view page named
hello-success.jsp that is located in WEB-INF/content (by default the Convention plugin expects all view pages to be
in this location). If the execute method returns “input” or “error” then the view page rendered would have been
hello-input.jsp or hello-error.jsp.
Struts Configuration Plugin
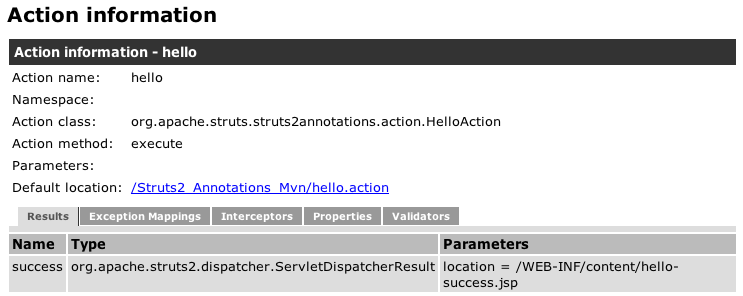
In a previous tutorial we reviewed how to use the Struts Configuration plugin to view the details of how Struts has configured your application. When using the Convention plugin, it’s very handy to also use the Configuration plugin during development. On the example application’s home page is a link to the application’s configuration. Click on that link and then the hello link on the left menu (under Actions in default). You’ll see the configuration for the hello action including it’s Action class, result, and view page.
Annotations
If you want to go beyond the simple naming conventions provided by the Convention plugin, you can use the Struts annotations also provided by the plugin. For example, a common work-flow for a Struts application is to first execute the ActionSupport class’s input method to setup form field default values and then to run the execute method of the same ActionSupport class when the form is submitted (to validate and save the user’s input).
The link to Register for the drawing on the example application’s home page follows this work flow. The link value
is register-input.action. If you examine the RegisterAction.java class you’ll find the input method with an Action annotation.
Action Annotation
@Action("register-input")
public String input() throws Exception {
logger.info("In input method of class Register");
return INPUT;
}
The Action annotation tells Struts to execute the annotated method when the action link value equals the Action
annotation’s value (register-input). So a link of register-input.action will call the input method of class RegisterAction.
On the example application’s home page is a link to Register for the drawing with a URL of register-input.action.
The input method above returns “input”. By the standards of the Convention plugin, the view page rendered will be
register-input.jsp (from WEB-INF/content). On that view page is a Struts form tag with an action attribute value
of register. When submitting the form, the execute method of class RegisterAction will be run. Since the execute method
returns success, the view page rendered is register-success.jsp.
Struts Configuration Values
In previous examples, we included in struts.xml values for some of the Struts configuration parameters.
struts.xml parameter configuration
<constant name="struts.devMode" value="true" />
When we don’t use a struts.xml file, we can set the value of these Struts parameters by using filter parameters in web.xml:
Struts Parameter Configuration web.xml
<filter>
<filter-name>struts2</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>struts.devMode</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
Summary
We’ve just scratched the surface of what the Struts convention plugin provides to reduce or eliminate the need to use an XML file to configure your Struts application. The Struts Convention plugin provides ways to map multiple actions to the same method, map results to different view pages, map errors to view pages, and much more. Be sure to read through the Convention Plugin documentation for alternative ways to configure your Struts application.
| Return to Spring and Struts | or | onward to Introducing Interceptors |
